In this article I'm gonna be talking about the mechanism of Linear Search Algorithm and how you can implement it in C.
I've already given you a brief introduction of this algorithm in my previous article. You can check it out here.
So, summing it all up - the Linear Search Algorithm is basically checking each element of an array one by one until you find the element you're searching for. If you're given an array of elements and you're expected to find a specific element from that array of elements, then this is the method that would come first in your mind.
The Algorithm
You might've observed that its not a very tough algorithm to understand. It's very straightforward. You just have to follow these simple steps for it-
-
Get an array of elements and the element you want to search in the array(let's say "s") from the user.
-
Start from the first element. Let's call it "i".
-
Start iterating over the array - ->Check if i==s:
->If yes -> Print "Element found"
->If no -> set i as the next element of i in the array, until you reach the end.
Our Amazing SponsorsDigitalOcean offers a simple and reliable cloud hosting solution that enables developers to get their website or application up and running quickly.View Website
Laravel News keeps you up to date with everything Laravel. Everything from framework news to new community packages, Laravel tutorials, and more.View Website
A Laravel Starter Kit that includes Authentication, User Dashboard, Edit Profile, and a set of UI Components. Learn more about the DevDojo sponsorship program and see your logo here to get your brand in front of thousands of developers.View Website
The code
The code for the above algorithm would look something like this -
void linearSearch(int s, int *arr, int n){
int flag = 0;
//iterate over the array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
//check equality
if(s == arr[i]){
//element found
flag = 1;
break;
}// otherwise move on to the next element in the array till the end.
}
//now check if the element was found or not
if(flag == 1){
printf("Element found!\n");
}else if(flag == 0){
printf("Element not found.\n");
}
}
Note that I've added an additional variable to check whether the element was found or not.
Basically, we first set its value as 0. Then, we check each element. If we find a match, its value is changed to 1 otherwise it remains 0. So if the element is not present in the array, it'll remain zero and therefore it'll show "Element not found".
Full code
The full code for the program is -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void linearSearch(int s, int *arr, int n){
int flag = 0;
//iterate over the array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
//check equality
if(s == arr[i]){
//element found
flag = 1;
break;
}// otherwise move on to the next element in the array till the end.
}
//now check if the element was found or not
if(flag == 1){
printf("Element found!\n");
}else if(flag == 0){
printf("Element not found.\n");
}
}
int main(){
int n, *arr;
printf("Enter the number of elements: ");
scanf(" %d", &n);
arr = (int *)malloc(n*sizeof(int));//allocating memory to the array
//Make an array
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
printf("Enter element: ");
scanf(" %d", &arr[i]);
}
//Get a search element;
int s;
printf("Enter the element you want to search for: ");
scanf(" %d", &s);
//Implement linear search
linearSearch(s, arr, n);
}
And finally, here are some gifs to make the algorithm easy to visualize-
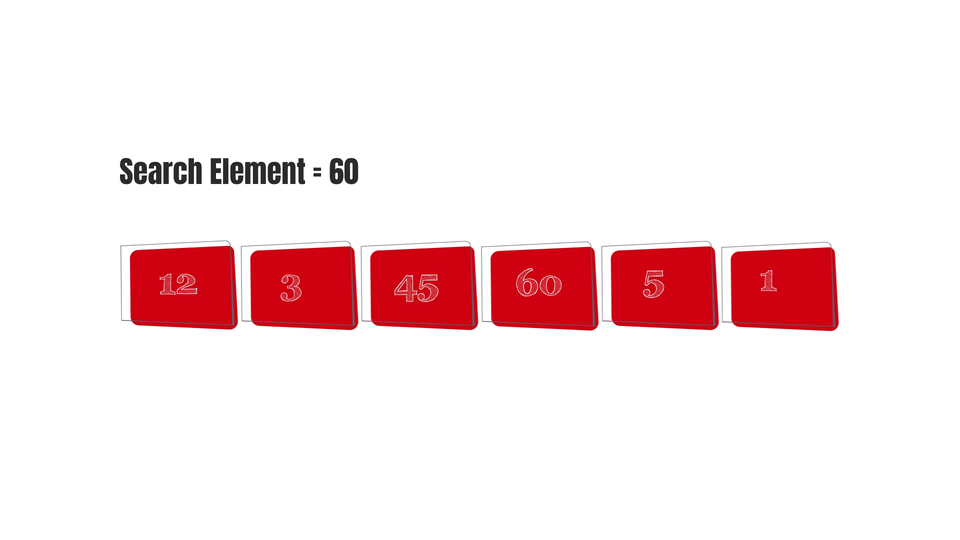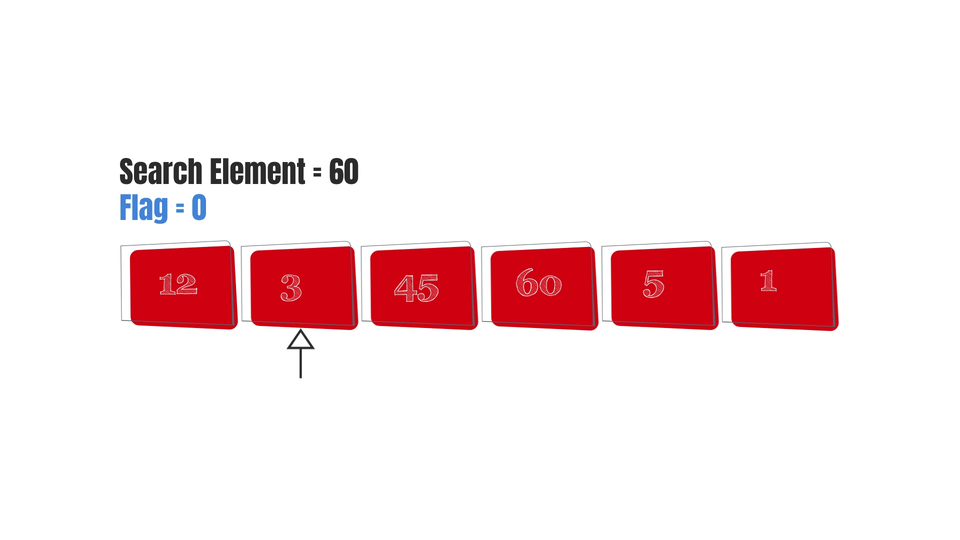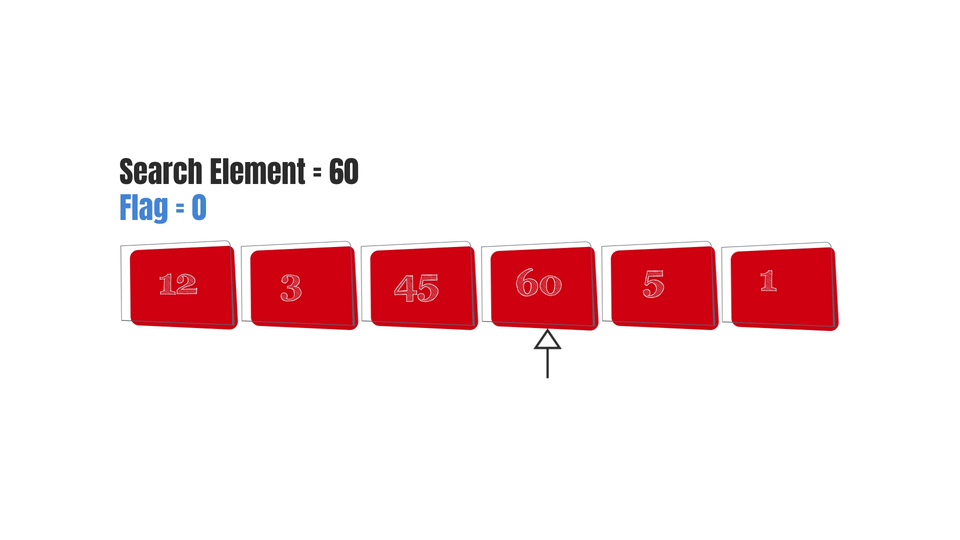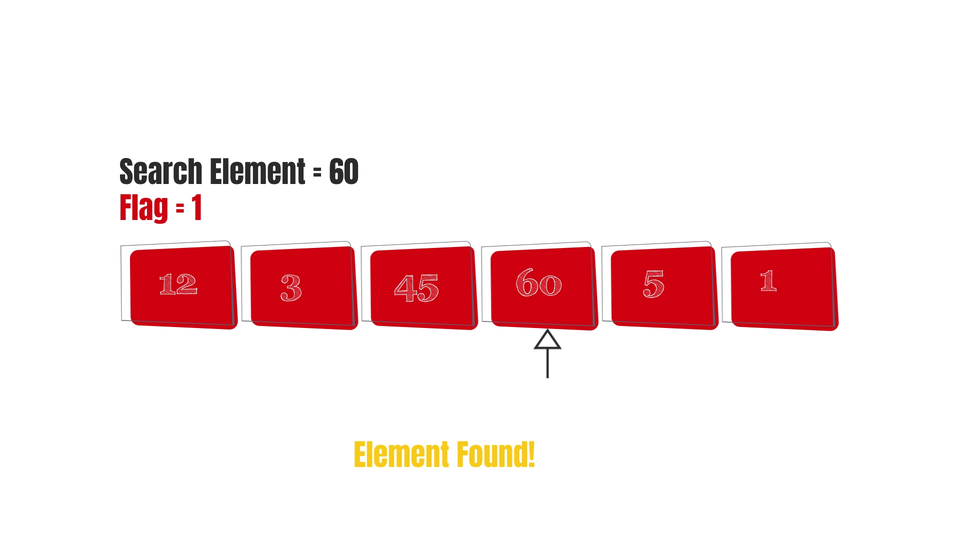
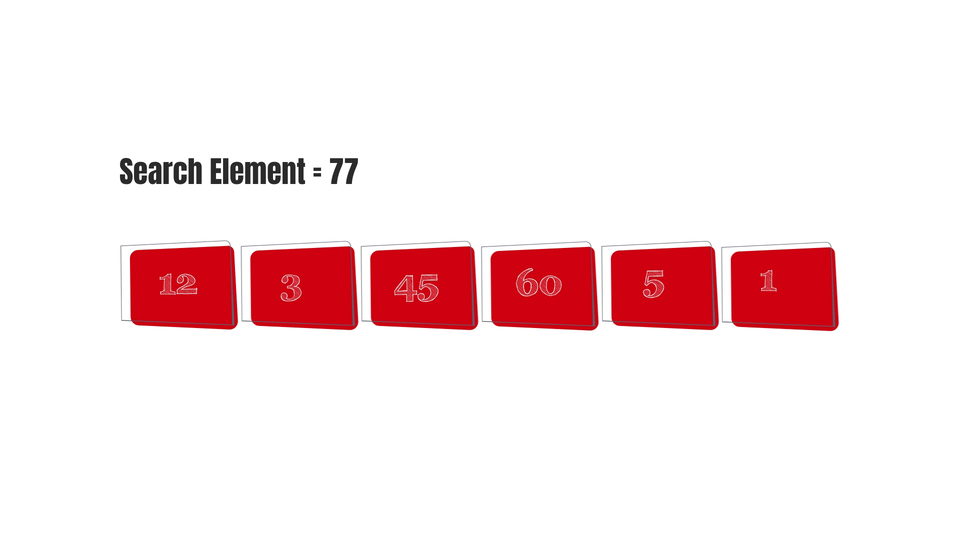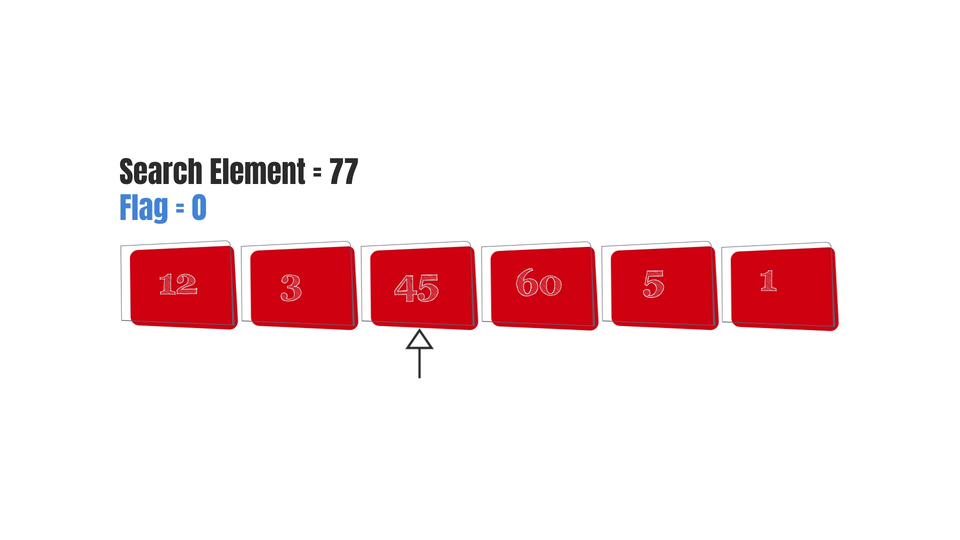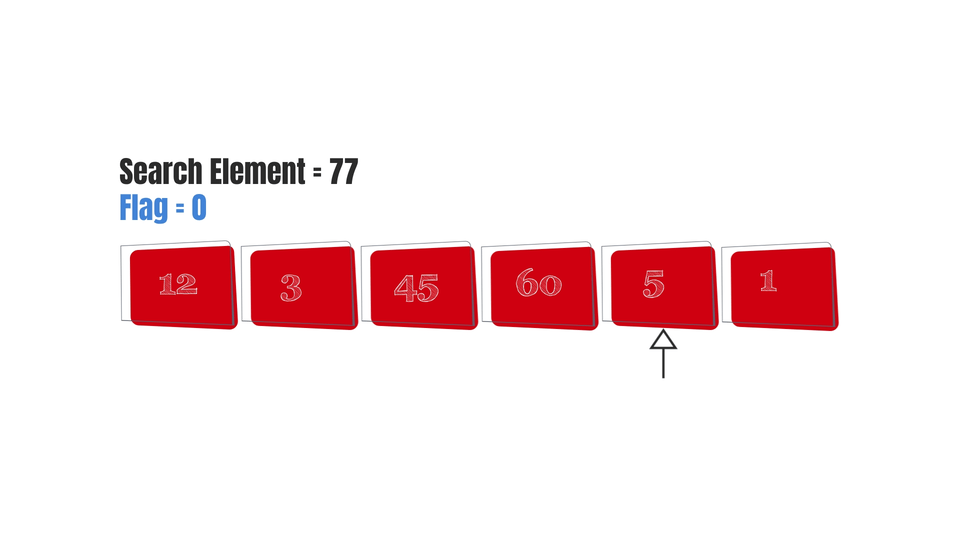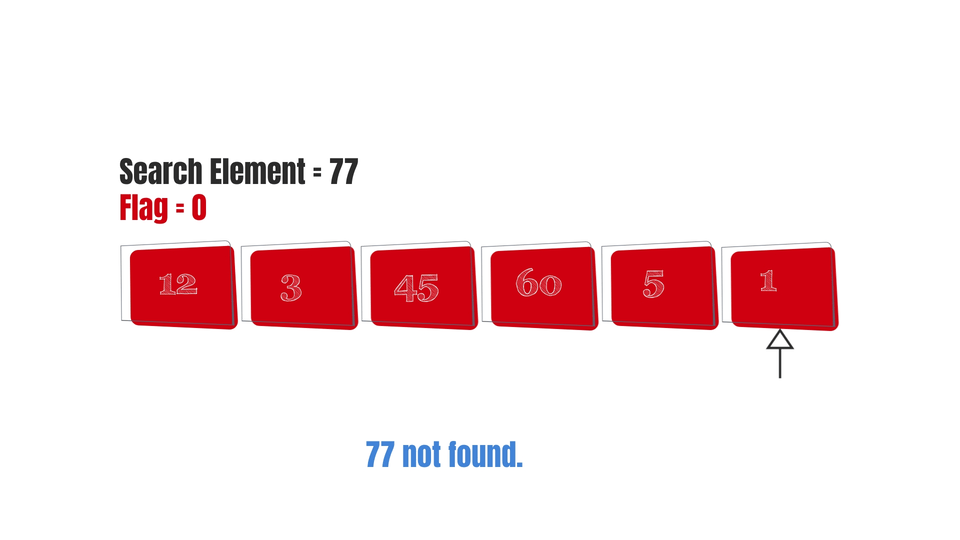
Conclusion
I've tried my best to put forward the concept of Linear Search through this post. I hope you liked reading it. You can check out my other posts here.
Thanks for reading!😊


Comments (0)