Introduction
Why using the Network-Manager's cli? Sometimes Ubuntu Network Manager can be really dodgy and you might be unable to connect to any Wi-Fi Hotspot via the GUI (Graphical user interface).
The Network-Manager may fail to start and even when manually restarting the service via the terminal you might still face issues to connect to any Wi-Fi Hotspot, even to an already known and saved home network.
I had that issue on dual boot setups and on standalone Linux installations and found it really annoying especially during the WFH (Working from home) period that we're all going through.
It’s really handy that the Network-manager has command-line tool for controlling the Network Manager. It’s called nmcli
nmcli gives you the opportunity to connect/disconnect and also do some other things with the Network-Manager like turning your PC into a Wi-Fi Hotspot itself. Here are the basics commands you need in order to connect to any available network.
General usage of the cli:
If you want to check all of your already saved connections run the following command:
nmcli c
In order to see the available Wi-Fi Hotspots, run the following command:
nmcli d wifi list
The output should be like this:
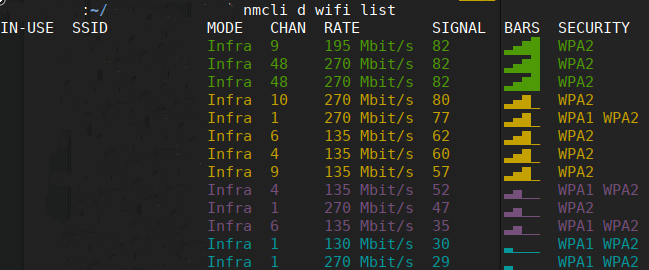
You can also use:
 View Website
View Website
 View Website
View Website
 View Website
View Website
sudo iwlist wlan0 scanning
Note You might need to change wlan0 with your actual interface, this can be checked easily with the ifconfig or iwconfig commands.
Another thing you can do is to list your network interfaces as this will be needed when you want to disconnect from a certain network:
iwconfig
The output should be like this:
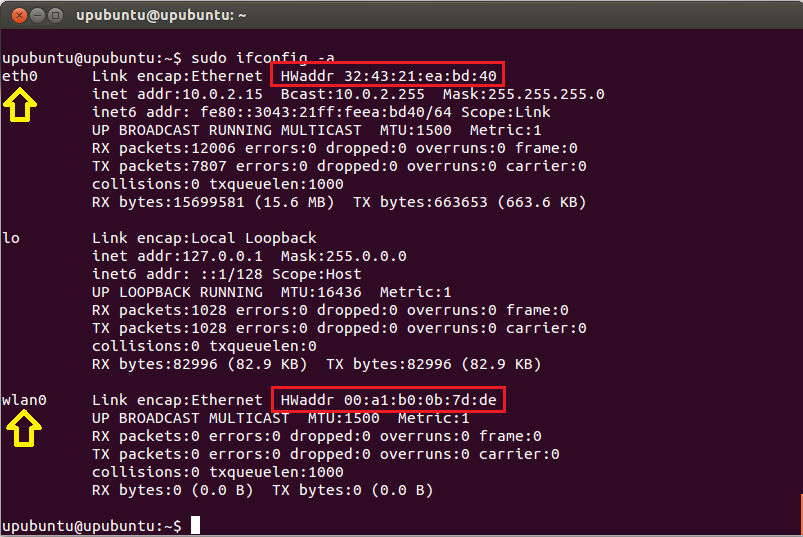
Now when you know your Wifi Interface you can easily disconnect it using the Network Manager’s cli using the following command:
nmcli d disconnect WifiInterface
and example is:
nmcli d disconnect wlan0
We’re using wlan0 since this is the network interface we’re using.
In order to connect you can use:
nmcli d connect WifiInterface
example:
nmcli d connect wlan0
However you can also use the following commands since you can also specify the exact Wi-Fi network you’re connecting to.
Note: Have in mind that this might only work on Ubuntu 16.04 – In order to disconnect use:
nmcli c down Wi-Fi-Name
example
nmcli c down Wi-Fi-Name
And in order to connect to a saved Wi-Fi network use:
nmcli c up Wi-Fi-Name
example:
nmcli c up Wi-Fi-Name
Conclusion
That's pretty much how you can now use nmcli to connect Wi-Fi networks
However if you face any issues feel free to send me an email with the error/issue that you’re facing and we can check it.
You can also check the full man page of the nmcli man page if you want to check all of the options available!


Comments (0)