Plug-ins
Wave offers a simple way to include additional funcitonality in your app with plug-ins.
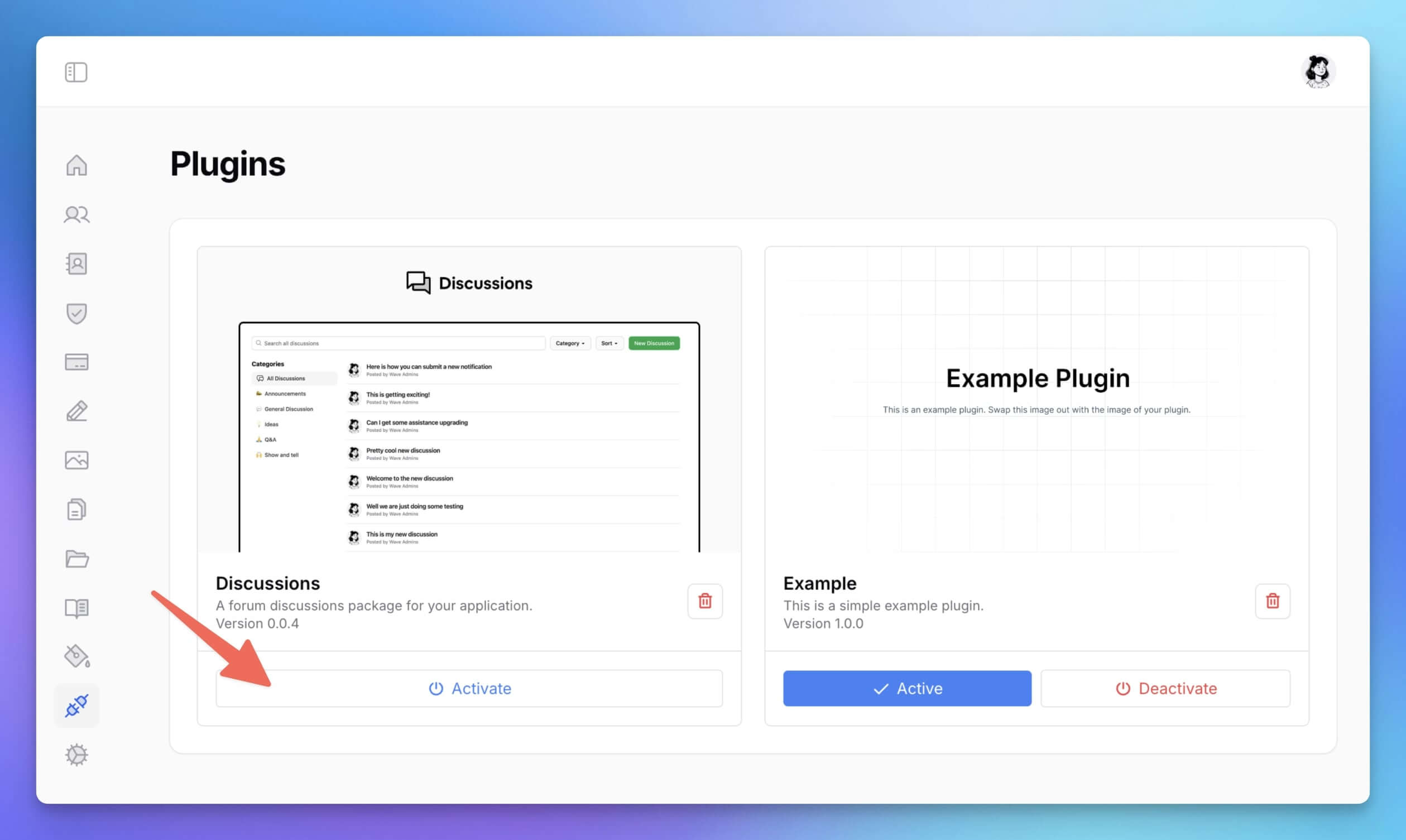
Installing Plugins
To install a Wave plugin, place the plugin folder inside the resources/plugins directory. For example, if you’re installing the discussions plugin, move its folder to resources/plugins/discussions. Once the folder is in place, navigate to the admin plugin section at /admin/plugins.
Here, you’ll see a list of available plugins. To activate one, simply click the Activate button under the plugin you would like to install.
How Plugins Work
Plugins are stored in the resources/plugins directory. Within this folder, you'll also find an installed.json file, this keeps track of the installed plugins. It contains an array of plugin names. For instance, if the discussions plugin is installed, the installed.json file would look like this:
[
"discussions"
]
The Plugin Class
At the core of each plugin is the main plugin class (e.g., example\ExamplePlugin.php), which acts as the entry point for each plugin. The ExamplePlugin.php file allows plugin developers to utilize the boot and register methods to add functionality to their application.
- Boot Method The
boot()method is where you add the main logic for your plug-in. Include any functionality you'd like to enhance your application with, such as loading components, views, or routes.
public function boot()
{
// Load views for the ExamplePlugin
$this->loadViewsFrom(__DIR__ . '/resources/views', 'example');
// Load migrations for the ExamplePlugin
$this->loadMigrationsFrom(__DIR__ . '/database/migrations');
// Load routes for the ExamplePlugin
$this->loadRoutesFrom(__DIR__ . '/routes/web.php');
// Register a Livewire component for the ExamplePlugin
Livewire::component('example-component', \App\Plugins\ExamplePlugin\Components\ExampleComponent::class);
}
The
bootmethod is called during the application startup process; however, you may need to register services or configs before the app is fully booted, in that case you'll use theregistermethod.
- Register Method The
registermethod is used to register services and/or include utilities. It runs before all other plugins have executed their boot functionality. Ideal for setting up anything your app will need.
public function register()
{
// Bind an interface to a concrete implementation
$this->app->bind('App\Contracts\SomeServiceInterface', 'App\Services\SomeService');
// Register a singleton service
$this->app->singleton('SomeUtility', function ($app) {
return new \App\Utilities\SomeUtility();
});
}
The Wave plugin system closely mimics the behavior of a Laravel package. The main Plug-in class extends the Laravel ServiceProvider class.
Autoloading
All classes and files inside the src folder of the plugin are autoloaded. This means you can easily organize your plugin's code into models, controllers, and other class types without worrying about manually including files.
The autoloading is handled by the plugin system's custom autoloader, which follows PSR-4 standards. For example, a class located at plugins/example/src/Models/Post.php would be autoloaded with the namespace Wave\Plugins\Example\Models\Post.
Plugin Loading Process
- The Wave application scans the
resources/plugins/installed.jsonfile to determine which plugins are installed. - For each installed plugin, the system instantiates the main plugin class (e.g.,
ExamplePlugin). - The
registermethod of the plugin is called, allowing it to register its services with the application. - After all plugins are registered, the
bootmethod of each plugin is called in turn.
This process ensures that plugins can interact with the Wave application just like built-in Laravel service providers, making it easy to extend and enhance the functionality of your Wave application.